- Researchers developed and tested nanoparticle eyedrops, combined with a laser process, which can improve both long and short sightedness.
- The technology may allow users to have their vision corrected without medical supervision.
You have asked for high-tech eye glasses and 3D printed bionic eyeball, but scientists have come with something even better. They have developed a vision-improving nanoparticle eyedrops that might end the need for contact lenses, eyeglasses, and laser correction of refractive errors.
According to the National Eye Institute, about 42% of Americans (from ages 12 to 54) are nearsighted (called myopia). Children living in urban environments are more than twice as likely to be myopic as compared to those living in rural environments. Whereas, farsightedness (called Hyperopia) can affect both adults and children. It affects about 5% to 10% of Americans, and people whose parents already have hyperopia are more likely to get the condition.
A research team of ophthalmologists at Shaare Zedek Medical Center and Bar-Ilan University, Isarel, have developed and tested “nanodrops”, along with a laser process, which can improve both long and short sightedness. Clinical testing will be done later in 2018.
How These Nanodrops Work?
In order to achieve correction and optical effect, nanodrops locally alter the corneal refractive index. These nanodrops go into the shallow ablated pattern produced on the cornea’s surface, and modify the refractive index inside those patterns, correcting the visual problem.
Specifically, the magnitude of the optical correction is configured through an optical pattern, which is stamped onto the epithelium superficial layer (on the cornea), with a laser source. The structure of optical pattern could be configured for correction of both myopia and hyperopia as well as presbyopia (associated with aging of the eye).
This laser stamping takes only a fraction of seconds (milliseconds) and enables the nanoparticles to “activate” and improve optical pattern by altering the reflective index, and eventually changing the light’s trajectory passing through the cornea.
How It’s Different?
The laser stamping source is quite different from conventional visual correction laser treatment that ablates thin tissue in the cornea. It’s a small laser equipment, which you can connect to your smartphone and stamp an optical pattern onto the epithelium of the cornea by placing multiple adjacent pluses. The overall process takes a few seconds and don’t cause any pain.
Source: Bar-IIan University | ESCRS
The small spots in the cornea produced by the laser enables biocompatible and synthetic nanodrops to enter and change to eye’s optical power at the target correction.
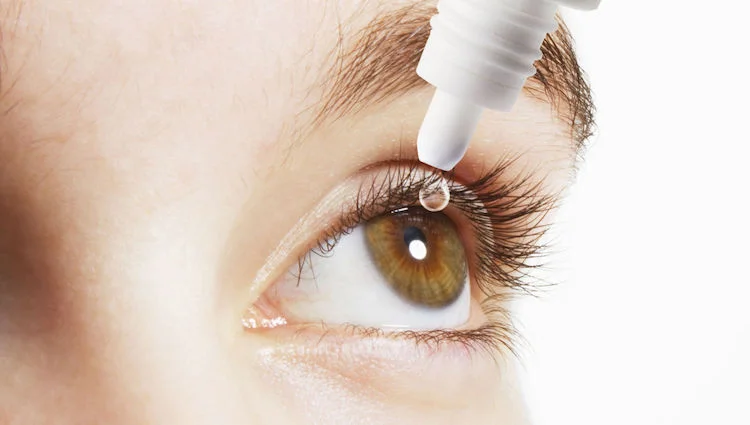
Downside
Since it’s a milder treatment, the technology has a downside – the eye will slowly heal itself. This means that the enhancements will gradually fade away. Thus, users would require to repeat the procedure every 1 or 2 months to maintain their improved vision.
Experiments Done So Far
Scientists have analyzed the refractive errors of 10 pig eyes using an automated refractometer. After putting nanodrops in their eyes, a mean correction of 1,96+/-0.2D and 2,24 +/-0.07D has been achieved for hyperopic and myopic refractive error, respectively.
There was no change in central keratometry of cornea. On average, encapsulated hyperreflective nanoparticules of diameter 0.58 nanometers were spotted throughout the first 60 microns thickness of the cornea.
Read: Artificial Eye Built With Adaptive Metalens and Supporting Muscle
So far, the technology has shown that it could correct about 3 diopters of myopia and presbyopia. Scientists plan to conduct experiments on rabbits to accurately figure out how long the nanodrops’ effect will last.
In coming years, this technique may allow users to have their vision corrected without medical supervision. They would measure their vision using a smartphone app, use laser device to stamp an optical pattern at the target correction, and apply nanoparticles to enable the pattern and get desired correction. This all can be done from the comfort of your own home.

Will it work for those with high myopia?
I read it will work for those who have power less than 7.