Only a few companies embody innovation across as many industries as 3M Company, the century-old American manufacturing giant that has quietly become one of the most versatile players in global business.
Its product portfolio exceeds 60,000 items, spanning nearly every aspect of daily life, from Post-it Notes and Scotch tape to medical adhesives and automotive films.
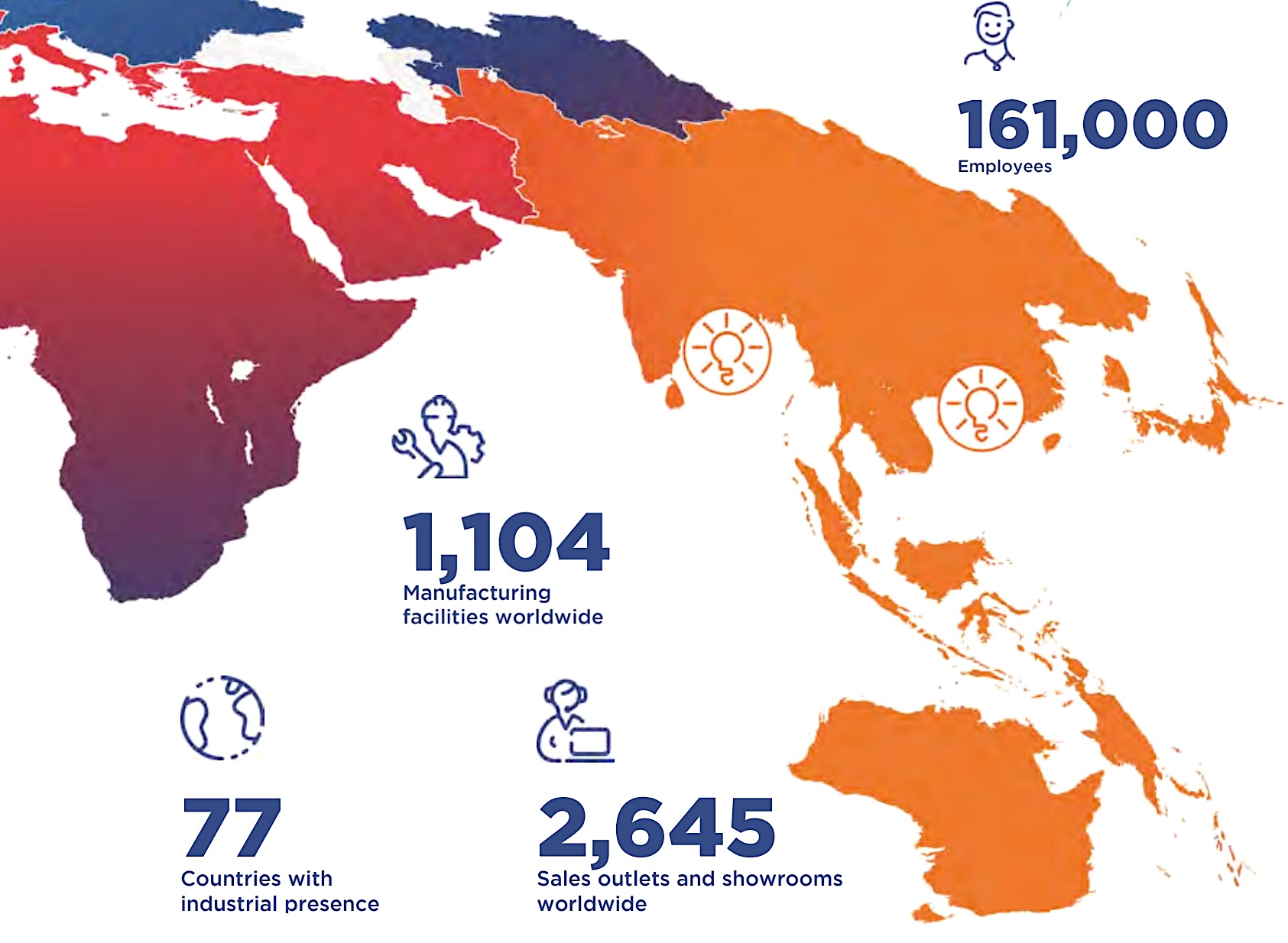
3M’s influence is backed by an immense global scale. It operates in over 200 countries, with manufacturing and R&D facilities spread across 50+ nations.
At the heart of 3M’s dominance lies its commitment to innovation. The company spends more than $1.1 billion in R&D every year. In its 120-year history, it has earned more than 120,000 patents worldwide and continues to file about 3,000 new ones annually, equivalent to nearly 8 new inventions every day. [1]
Yet, despite its dominance, 3M operates in one of the most competitive and rapidly evolving sectors. Its rivals collectively control a multi-trillion-dollar global industrial and advanced materials market, where innovation cycles are accelerating and digital manufacturing is reshaping production efficiency.
Below, I present 3M’s top competitors across its major business divisions, analyzing where each firm’s competitive edge lies, and how innovation and diversification continue to redefine this global industrial rivalry.
Did you know?3M is a leader in the global industrial adhesives market, which is projected to reach $98.4 billion by 2030, driven by demand in automotive, construction, and electronics. [2]

Table of Contents
13. Mapei S.p.A
Founded in 1937Headquarters: Milan, Italy
Revenue: $5 billion+
Competitive Edge: Specialization in building-industry chemical systems
Mapei produces chemical products for the building industry, particularly adhesives, sealants, and chemical additives for construction.
Its product range covers a broad spectrum of construction applications, including tile and stone installation systems, waterproofing solutions, concrete repair and strengthening, industrial flooring, and wall coatings.
The company offers highly tailored solutions that meet the unique technical requirements of construction projects. Plus, its close collaboration with architects, civil engineers, and contractors gives it a consultative edge over more diversified rivals like 3M.
Mapei emphasizes innovation, sustainability, and local-for-local manufacturing. It has 38 research centers across five continents and achieved strong growth in 2024, particularly in Latin America (+28.3%) and the Middle East (+130.3%). [3]
In 2025, Mapei was recognized by TIME magazine as one of the “World’s Best Companies” for its growth, innovation, and global footprint.
12. Parker Hannifin Corporation
 Parker Hannifin’s global headquarters in Ohio
Parker Hannifin’s global headquarters in Ohio
Headquarters: Ohio, United States
Revenue: $19.8 billion+
Competitive Edge: Engineering expertise, Vertical integration
Parker Hannifin Corporation is one of the world’s largest and most diversified manufacturers of motion and control technologies. Its engineering solutions power and regulate motion across various industries through advanced fluid handling systems, filtration technologies, and hydraulic controls used in aircraft, heavy machinery, and industrial robotics.
The company makes hundreds of thousands of components, making it one of the most vertically integrated manufacturers in the global industrial supply chain.
Parker’s scale and influence are immense: it holds more than 12,000 patents, with more than 40% still active. It operates through a global network of 13,000 distribution partners and serves more than 450,000 customers, ranging from small OEMs to large multinational corporations.
As a competitor to 3M, Parker Hannifin operates in overlapping areas such as filtration systems, industrial adhesives and sealants, fluid management, and materials engineering. For example, in filtration and sealing, Parker Hannifin’s products directly compete with 3M’s filtration membranes, industrial filters, and fluid management solutions.
Both companies also compete in the field of industrial adhesives, coatings, and performance materials, where Parker’s Engineered Materials Group offers sealing, thermal management, and vibration-control products that compete with 3M’s advanced materials and bonding technologies.
In FY 2025, Parker Hannifin reported revenue of $19.85 billion, a gross profit of $7.31 billion, and a net income of $3.53 billion. [4]
11. Akzo Nobel N.V
Founded in 1994Headquarters: Amsterdam, Netherlands
Revenue: $12 billion+
Competitive Edge: Color and Material Science leadership
Akzo Nobel manufactures paints, coatings, and specialty chemicals. It is recognized for its strong heritage of innovation, color technology, and sustainable chemistry.
The company has two main business divisions: Decorative Paints and Performance Coatings. Its diverse product portfolio includes well-known brands such as Dulux, Sikkens, International, Interpon, and Hammerite, which hold leading positions in both consumer and industrial markets.
As a competitor of 3M, Akzo Nobel operates in overlapping domains of industrial coatings, adhesives, surface protection, and specialty chemicals. Both companies compete in the automotive and aerospace coatings markets, where innovation in lightweight materials and environmental compliance is essential.
Akzo Nobel’s Interpon powder coatings and 3M’s automotive finishing systems often serve the same client base, including OEMs, aerospace manufacturers, and industrial fabricators. Similarly, in protective coatings and sealants, Akzo Nobel’s products rival 3M’s industrial adhesives and corrosion-resistant materials, especially in the marine and oil & gas sectors.
10. Saint-Gobain
Headquarters: Courbevoie, France
Revenue: $55 billion+
Competitive Edge: Brand legacy and technical expertise in glass and ceramics
Saint-Gobain is one of the world’s oldest and most diversified industrial manufacturing companies, with a history spanning more than 3.5 centuries.
Founded in 1665 under the reign of King Louis XIV to produce glass for the Palace of Versailles, the company now serves both industrial and consumer markets with a wide portfolio of materials ranging from glass and insulation to mortars, polymers, abrasives, and high-tech ceramics.
Saint-Gobain’s products are integrated into everything from skyscrapers and cars to wind turbines and smartphones. The company benefits from massive economies of scale and an integrated global supply chain that allows it to manage costs more effectively than smaller competitors.
Saint-Gobain’s Norton Abrasives line competes directly with 3M’s Precision-Shaped Grain abrasives, both serving the automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication industries. In the adhesives and sealants category, Saint-Gobain’s Weber and High-Performance Materials segments rival 3M’s industrial bonding solutions for infrastructure and manufacturing.
Geographically, more than two-thirds of the Group’s pro forma operating income is now generated in high-growth regions: North America, Asia, and emerging markets. In 2024, the Group reported sales of roughly €46.6 billion and a net income of about €2.84 billion.
9. Huntsman Corporation

Headquarters: Texas, United States
Revenue: $6 billion+
Competitive Edge: Industrial-grade performance chemistry
Huntsman Corporation has three major business divisions: Polyurethanes, Performance Products, and Advanced Materials. The Polyurethanes division produces materials essential to the creation of foams, insulation panels, automotive seats, coatings, and adhesives.
The Performance Products segment supplies chemical intermediates and amines used in detergents, electronics, and oilfield services. Meanwhile, Advanced Materials focuses on high-performance adhesives, composites, and epoxy resins.
The company operates over 60 manufacturing, R&D, and operations facilities in 25+ countries and directly employs around 6,300 associates in its continuing operations.
It competes with 3M in the fields of advanced adhesives, performance coatings, and engineered materials. While 3M has a broad, diversified portfolio spanning healthcare, electronics, and safety, Huntsman’s strength lies in chemical innovation and specialty materials for industrial and structural applications.
Huntsman’s strategic focus is on high-margin specialty materials rather than commodity chemicals. The company has steadily transitioned toward performance materials that deliver higher returns and align with long-term sustainability trends.
8. Dow Inc
Headquarters: Michigan, United States
Revenue: $41.8 billion+
Competitive Edge: Scale & integration; Leadership in polymer chemistry and silicone adhesives
Dow Inc. is one of the world’s largest and most influential materials science companies, with a diverse product range spanning chemicals, plastics, coatings, and advanced materials.
Dow’s industrial adhesives and specialty chemicals challenge 3M’s bonding and coating products in several applications. For instance, Dow’s silicone adhesives and sealants rival 3M’s industrial tapes and bonding systems in electronics, aerospace, and automotive manufacturing. Similarly, Dow’s polyurethane-based and epoxy adhesives are direct competitors to 3M’s structural bonding solutions.
The company invests roughly $800 million annually in R&D, leveraging a robust innovation pipeline to stay ahead in performance materials and specialty chemicals. It has pioneered advanced polymers, silicone-based technologies, and high-strength adhesives used in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and renewable energy sectors.
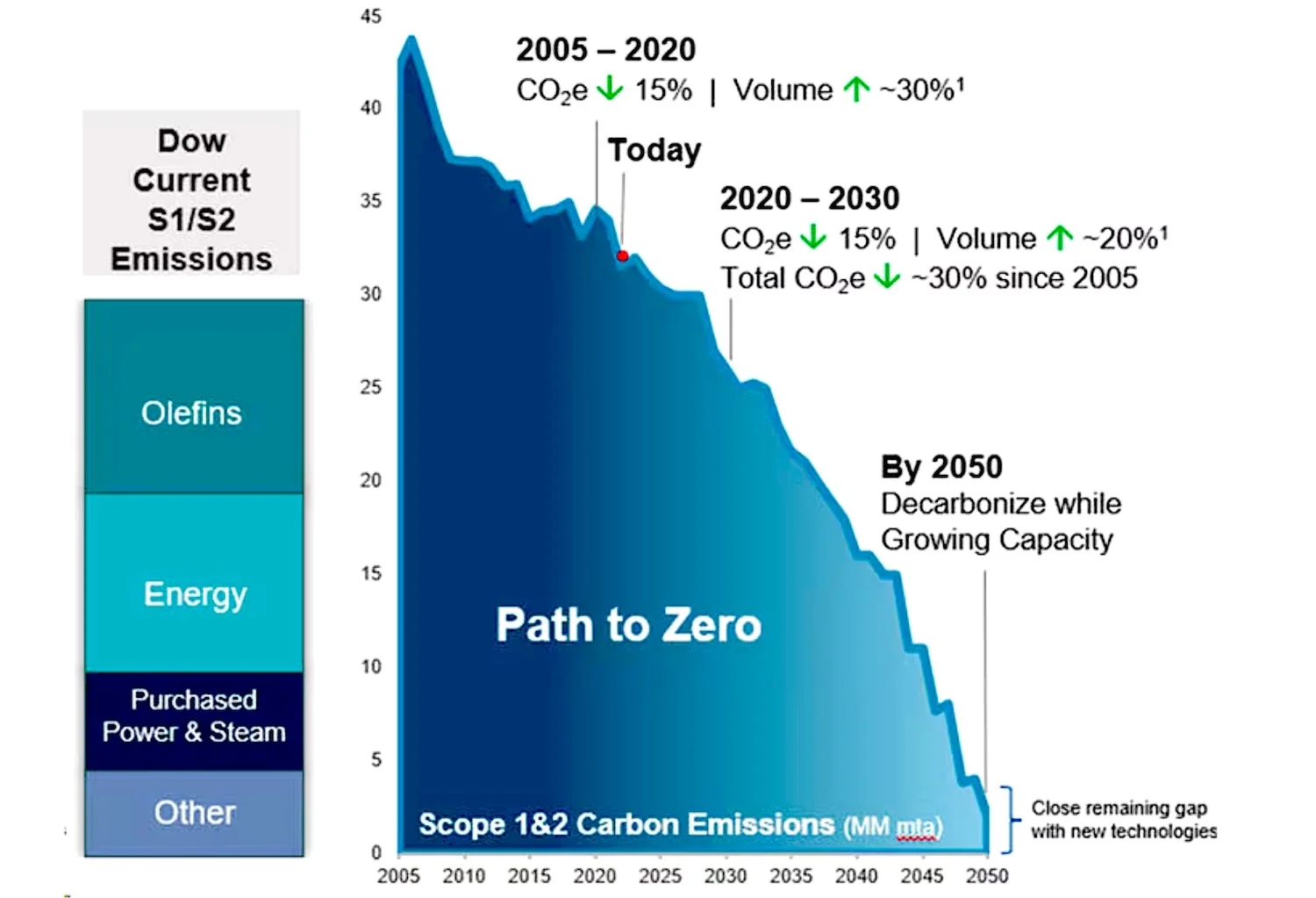
Dow’s core strategy revolves around sustainable chemistry, circular economy practices, and carbon reduction, aligning its product innovation with global ESG trends. The company aims to achieve neutrality by 2050 and has already made major progress toward a 30% emissions reduction by 2030. [5]
7. Avery Dennison Corporation

Headquarters: Ohio, United States
Revenue: $8.7 billion+
Competitive Edge: Global market leader in RFID tagging, Material science expertise
Avery Dennison is a global materials science and manufacturing company best known for its labeling, packaging materials, and adhesive technologies. Their products are used daily in billions of items worldwide, from retail price tags and barcodes to RFID tracking systems and industrial films.
The company generates over $8.5 billion annually, driven by consistent growth from e-commerce expansion, digital labeling demand, and supply chain automation.
Avery Dennison’s global success is driven by its innovation in materials science and adhesive chemistry. The company holds over 9,240 patents worldwide, with more than 48% of them active. These patents cover advanced films, coatings, and adhesive technologies. [6]
The company has expanded its capabilities in digital identification and data-driven labeling, investing heavily in RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology to help retailers and logistics companies improve supply chain visibility.
Its RFID business alone now serves top-tier clients such as Nike, Walmart, and Decathlon, integrating smart tracking technology into billions of apparel items annually.
6. H.B. Fuller Company

Headquarters: Minnesota, United States
Revenue: $3.5 billion+
Competitive Edge: Specialisation and engineering-intensive solutions
H.B. Fuller Company manufactures industrial adhesives, sealants, and specialty chemical products. Its portfolio spans a wide range of bonding and sealing technologies such as hot melt, water-based, reactive, and pressure-sensitive adhesives.
Fuller’s strength lies in its high level of customization and technical service, offering bespoke formulations that meet unique industrial needs — something that 3M’s mass-scale approach does not always provide.
It serves diverse industries, including packaging, construction, electronics, automotive, hygiene, aerospace, and renewable energy.
Over the years, the company has grown through strategic acquisitions, including major deals like Royal Adhesives & Sealants in 2017 and Wisdom Worldwide Adhesives in 2022. In 2024, it further expanded its Medical Adhesive Technology segment with the acquisitions of GEM S.r.l. and Medifill Ltd.
Today, Fuller employs around 7,500 people across 81 manufacturing sites in 26 countries. The company plans to streamline its manufacturing and supply chain operations, aiming to reduce the number of plants to 55 by 2030 and achieve annual cost savings of about $75 million. [7]
5. Sika AG
Headquarters: Baar, Switzerland
Revenue: $14 billion+
Competitive Edge: Specialised bonding/sealing expertise
Sika AG is a Swiss multinational specialty chemicals company known for its expertise in construction materials, adhesives, sealants, and industrial bonding technologies. It develops systems for sealing, bonding, damping, reinforcing, and protecting load-bearing structures.
In the industrial and transportation sectors, Sika’s products directly challenge 3M’s offerings. Sika supplies adhesives used in vehicle body assembly, EV battery housing, and lightweight composite bonding, competing with 3M’s industrial adhesive tapes and sealants.
In the construction sector, Sika’s high-performance sealants and concrete admixtures rival 3M’s architectural coatings and protective films.
Sika allocates about 2.5% of its revenue to R&D. Its patent portfolio includes 1,606 unique patent families and 5,772 individual national patents. [8]
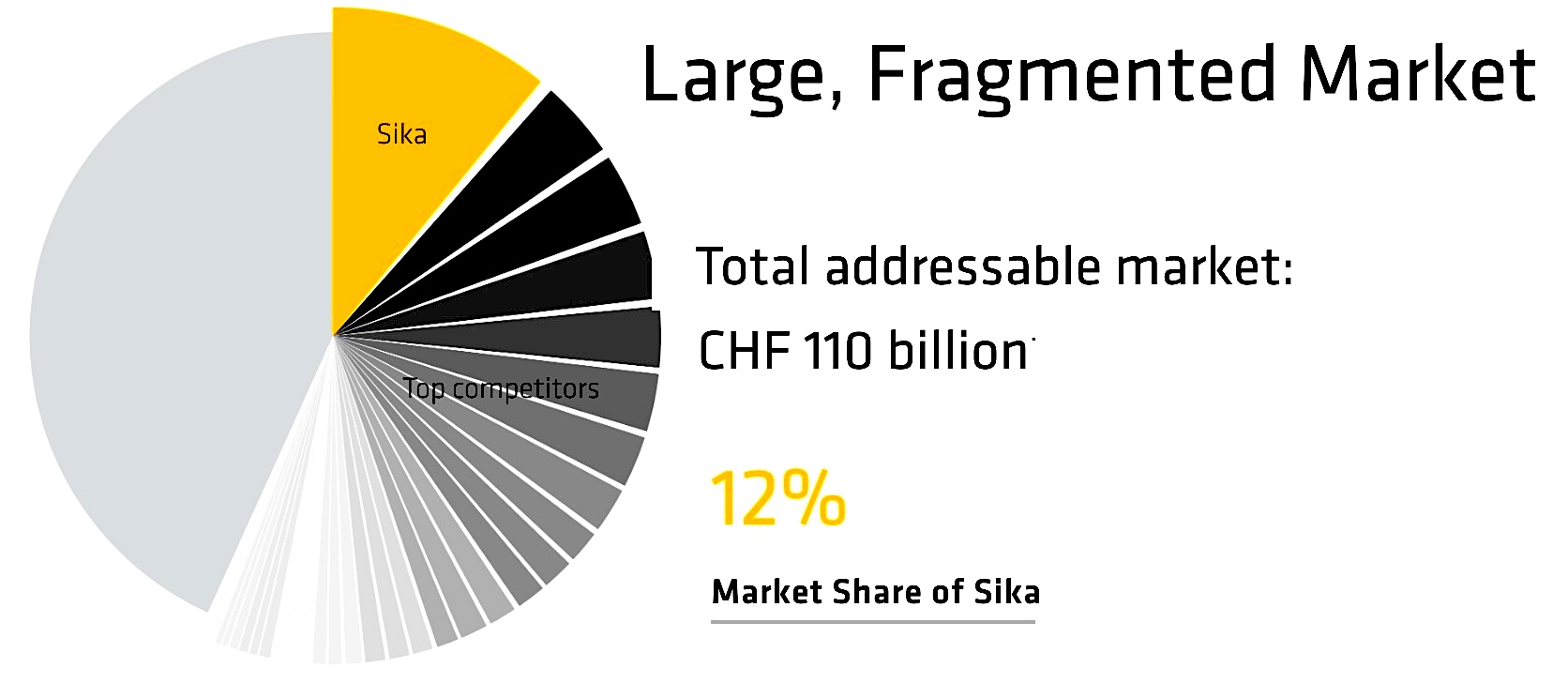
The company operates in over 100 countries with more than 400 production sites and around 32,000 employees. Its customers include major construction contractors, automakers, packaging companies, and energy firms.
In 2024, Sika reported net sales of CHF 11.76 billion, up about 4.7% in Swiss francs, while net profit rose 17.4% to around CHF 1.24 billion. In 2025, the company announced strategic investment and expansion of its manufacturing footprint in China, Brazil, and Morocco to strengthen its “local-for-local” strategy.
4. BASF
 Ludwigshafen production site
Ludwigshafen production site
Headquarters: Ludwigshafen, Germany
Revenue: $25.6 billion+
Competitive Edge: Verbund integration system, R&D scale and scientific depth
BASF’s scale is unparalleled in the chemical industry. It employs approximately 111,000 people worldwide and generates more than €65 billion in annual revenue, making it the largest chemical producer globally by sales.
Its business model spans the full value chain, from basic chemicals and intermediates to high-value specialty materials and crop solutions. The company’s products are found in coatings, plastics, catalysts, agricultural inputs, adhesives, battery components, and construction materials.
While 3M excels in multi-disciplinary applied science (combining chemistry with electronics and healthcare), BASF’s strength lies in core chemical engineering and molecular material innovation.
A key driver of BASF’s success is its integrated “Verbund” system, a production and logistics network that connects its plants to maximize resource efficiency. This system allows by-products from one process to serve as feedstock for another, drastically reducing waste and energy consumption.
Its Ludwigshafen site alone is considered the world’s biggest integrated chemical complex, spanning over 10 square kilometers and hosting more than 200 interconnected production facilities.
BASF invests over €2 billion annually in R&D, supported by a global team of over 11,000 scientists and engineers. It holds over 83,600 patents globally, covering advanced polymers, catalysts, and sustainable materials. Most of these patents are filed in Europe, followed by the USA and China. [9]
The company has also pledged to achieve net-zero CO₂ emissions by 2050 and to increase the share of renewable energy and circular materials in its production mix.
3. Henkel
Headquarters: Düsseldorf, Germany
Revenue: $25.6 billion+
Competitive Edge: Strong brand and technology portfolio
Henkel’s long-standing commitment to science-driven innovation and brand diversification has allowed it to sustain a global presence for nearly 150 years.
Its business spans across three primary divisions: Adhesive Technologies, Beauty Care, and Laundry & Home Care. The Adhesive Technologies division is the company’s core strength, accounting for nearly half of its total revenue.
Its adhesives are found in electronics, automotive manufacturing, aerospace, construction, packaging, and consumer goods. The company’s well-known consumer brands include Persil, Schwarzkopf, Loctite, and Purex, many of which hold leading market shares in their respective categories.
Henkel’s commitment to innovation is reflected in the fact that it owns over 7,000 patents. Plus, it has registered 4,008 trademarks, with the most common category being “polishing, cleaning, bleaching, scouring, and abrasive preparations; cosmetics.”
In 2024, Henkel generated sales of €21.6 billion, representing an organic sales growth of about 2.6%. The operating profit rose significantly by about 20.9% to €3.1 billion, yielding an EBIT margin of 14.3%. It also reported a strong free cash flow of about €2.4 billion. [10]
2. DuPont de Nemours

Headquarters: Delaware, United States
Revenue: $12.6 billion+
Competitive Edge: Materials Science leadership, Focus on high-growth end-markets
DuPont is one of the oldest and most influential science and materials companies in the world. DuPont operates in 70+ countries, serving industries from semiconductors and transportation to construction, packaging, and healthcare.
DuPont’s long history of reinvention is unmatched: from pioneering nylon and Kevlar in the 20th century to developing high-performance films, water filtration systems, and semiconductor materials in the 21st.
The company holds more than 16,800 patents, with over 9,900 granted and more than 63% of them active. Most of these patents are filed in the United States, followed by China and South Korea.
In adhesives and electronics, DuPont directly challenges 3M’s electronics & energy division. Its advanced polyimide films, dielectric materials, and conductive adhesives are critical in flexible circuits, displays, and microchips.
In safety and protection, DuPont’s globally renowned Kevlar, Nomex, and Tyvek brands compete head-to-head with 3M’s safety and industrial segment. While 3M produces respirators, protective coatings, and films, DuPont dominates the protective garments and high-strength fibers markets used in aerospace and defense, and firefighting.
In water and filtration, DuPont’s FilmTec membranes and reverse-osmosis systems rival 3M’s filtration technologies in industrial and municipal applications.
The company has pledged to achieve carbon-neutral operations by 2050 and invests in circular-economy solutions across its global supply chain. [11]
1. Honeywell International

Headquarters: North Carolina, United States
Revenue: $39.99 billion+
Competitive Edge: Strong R&D and Patent pipeline
Honeywell International is one of the world’s most diversified technology and manufacturing conglomerates, employing more than 102,000 people. It competes with 3M across several overlapping business domains — most notably in industrial safety products, advanced materials, and smart manufacturing technologies.
In the safety and industrial segment, Honeywell’s protective gear, respirators, and sensors directly challenge 3M’s product lines in personal protective equipment (PPE) and industrial safety solutions.
In performance materials and technologies, Honeywell competes head-to-head with 3M’s industrial and electronics divisions. Both companies innovate in areas like advanced polymers, coatings, adhesives, and filtration technologies. However, Honeywell’s specialization in high-performance chemicals and process solutions gives it an edge in energy and petrochemical markets.
The firm has explicitly aligned itself with automation, aviation, and energy transition. These sectors provide strong tailwinds (driven by trends like more efficient aircraft, smart buildings, and IoT, and global decarbonization efforts).
In 2024, Honeywell invested a record $14.6 billion in capital, with about $8.9 billion directed toward acquisitions, reflecting an aggressive M&A and portfolio optimization strategy. [12]
In FY 2025, the company reported $39.99 billion in revenue, up 7.11% YoY. Its market capitalization is around $137 billion, and its enterprise value is close to $161 billion.
Read More
- 16 Largest Chemical Companies In The World
- 13 Largest Battery Manufacturers In The World
- 18 Best Science And Technology Research Labs In The World
- Research & Development, We invest about 5.9 percent of our sales in R&D, 3M
- Industry Report, Adhesive market size and trend analysis, Mordor Intelligence
- Road to Growth, Mapei achieves consolidated turnover of 4.4 billion euros, Mapei
- Company Highlights, Parker-Hannifin’s net income throughout the years, Macrotrends
- Purpose in Action, Decarbonization and climate mitigation, Dow Inc
- Company Analysis, Avery Dennison holds 9241 patents worldwide, Greyb
- Financial Report, H.B. Fuller reports Q4 and FY 2024 results, H.B. Fuller
- Innovation, Sika again among the Top 10 Swiss Companies that filed Patents with the EPO, Sika Group
- Company Analysis, BASF holds 83634 patents worldwide, Greyb
- Financial Report, Successful implementation of purposeful growth agenda, Henkel
- Press Release, DuPont commits to net-zero emissions by 2050, DuPont
- Press & Media, Honeywell Announces FY 2024 results and issues 2025 guidance, Honeywell


