Founded in 1889, Nintendo is one of the oldest entertainment companies in the world, predating film, television, and video games by decades.
To date, the company has sold more than 870 million hardware units worldwide, including both consoles and handhelds. The Nintendo Switch leads the pack, with more than 154 million units sold. It has also sold over 6 billion individual games. [1]
While the company is best known for its iconic family-friendly IP and hardware innovation, it competes with rivals that pursue vastly different strategies, including raw computing power, subscription ecosystems, and multimedia convergence.
In the sections below, I’ll highlight Nintendo’s top competitors and explain how each one competes with Nintendo in terms of hardware, software, services, intellectual property, revenue models, and long-term market position.
Did you know?The video game industry makes much more money than the global film industry. In 2024, gaming generated around $184 billion, compared to about $34 billion from movies. Looking ahead, the global gaming market is projected to reach $435 billion by 2030, growing at a 10.4% CAGR. [2][3]

Table of Contents
13. Roblox Corporation
Founded: 2004Headquarters: San Mateo, California, USA
Revenue: $4.4 billion+
Key Titles: Brookhaven, Blox Fruits
Competitive Edge: Metaverse-like social platform, Diversified monetization
Roblox Corporation operates one of the world’s largest user-generated gaming platforms, blurring the lines between a game publisher, a social network, and a digital economy.
On this platform, users can build, share, and play millions of different 3D experiences created by other users. They can even use the built-in Roblox Studio tools to design games and monetize their creations using the platform’s virtual currency called Robux.
Compared to Nintendo, which focuses on curated, premium experiences, Roblox captures daily engagement from younger players, many of whom treat the platform as a social hangout rather than a game.
A substantial portion of Roblox’s audience consists of Gen Z and Gen Alpha users, many of whom spend hundreds of hours per year inside the platform. The platform has steadily expanded its user base over the years, with average daily active users (DAUs) reaching about 82.9 million in 2024.
In 2025, the company raised its bookings forecast, fueled by viral hits like Grow a Garden and a sharp increase in player spending. As a result, DAUs crossed 150 million, marking Roblox’s biggest user growth jump in the past five years.
12. Scopely

Headquarters: Culver City, California, USA
Revenue: $3 billion
Key Titles: Monopoly GO, Stumble Guys
Competitive Edge: Mobile market leadership, Proprietary tech & analytics
Scopely is one of the world’s most profitable mobile-first gaming companies, built almost entirely around live-service, free-to-play titles. It focuses on mid-core mobile games designed for long-term engagement, rather than short, one-off experiences.
Scopely has reached over $10 billion in lifetime revenue and more than 1 billion total downloads. Several of its game franchises have each surpassed $1 billion in revenue.
The company distinguishes itself with a proprietary technology platform, Playgami, which supports game development, live operations, analytics, marketing, and community growth. This platform enables deep engagement and long-term monetization across its portfolio.
Scopely’s portfolio includes popular titles such as Monopoly GO!, Stumble Guys, Marvel Strike Force, Star Trek Fleet Command, Scrabble GO, WWE Champions, and Bingo Bash. The Monopoly GO!, in particular, achieved extraordinary success, reportedly generating over $6 billion in lifetime in-app purchase revenue. [4]
In 2025, Scopely acquired Niantic’s gaming division for $3.5 billion. This deal significantly expanded Scopely’s portfolio, adding major titles like Pokémon GO, Pikmin Bloom, Monster Hunter Now, along with several companion apps. [5]
11. Nexon
Founded: 1994Headquarters: Tokyo, Japan
Revenue: $3 billion+
Key Titles: MapleStory, Dungeon & Fighter
Competitive Edge: Excels in managing long-lifecycle games
Nexon is a South Korean-Japanese video game developer and publisher best known for pioneering free-to-play, online, and live-service game models.
Its strength lies in longevity and monetization mastery. Many of its games remain commercially relevant 15-20 years after launch, thanks to frequent updates, events, and deep player economies.
Nexon’s popular titles, such as MapleStory, Dungeon & Fighter, KartRider, The First Descendant, andBlue Archive, are among the longest-running online games. Dungeon & Fighter alone has garnered over 850 million players worldwide and generated $22+ billion in lifetime revenue. [6]
In 2025, Arc Raiders became the most successful global launch in Nexon’s history, selling over 4 million copies and reaching 700,000+ concurrent players. [7]
Nexon now plans to transition select franchises to console and cross-platform formats, aiming to reach audiences traditionally dominated by Nintendo and other console manufacturers.
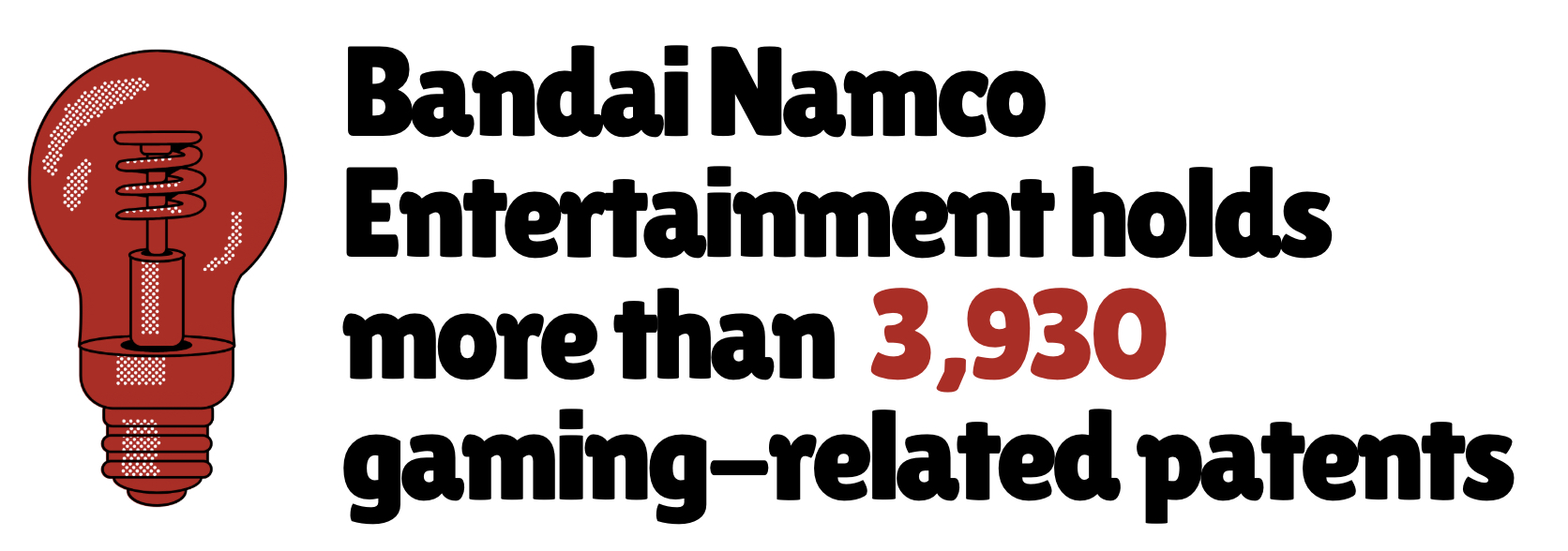
10. Bandai Namco Entertainment
Headquarters: Tokyo, Japan
Revenue: $3.2 billion+
Key Titles: Pac-Man, Tekken
Competitive Edge: Cross-platform publishing, Anime integration
Bandai Namco Entertainment is Japan’s strategically diversified entertainment company, operating across video games, toys, anime, licensing, and live events.
Unlike pure-play publishers, it monetizes intellectual property across multiple formats simultaneously, creating powerful feedback loops between games, merchandise, and media.
The company owns and publishes many multi-million-selling and culturally iconic franchises, including Pac-Man, Tekken, Ace Combat, Tales, Soulcalibur, Dark Souls, The Idolmaster, and numerous anime-licensed games based on Dragon Ball, Naruto, Gundam, and One Piece.
Financially, Bandai Namco balances mid-budget releases with occasional blockbuster bets, avoiding the extreme capital exposure seen in Western AAA publishers.
While exact revenue figures for the Entertainment division alone are not always publicly disclosed, its parent, Bandai Namco Holdings, generated over $8.1 billion in revenue in 2025, driven by strong digital business performance. [8]
9. Take-Two Interactive
 GTA VI Character
GTA VI Character
Headquarters: New York City, USA
Revenue: $6.2 billion+
Key Titles: Kerbal Space Program, Grand Theft Auto
Competitive Edge: Strong portfolio of AAA franchises, Creative autonomy
Take-Two Interactive is one of the most profit-dense publishers, operating fewer franchises than most competitors but extracting extraordinary lifetime value from each.
The company has built its reputation around blockbuster, culturally defining titles rather than high-volume annual releases. Its crown jewel is Grand Theft Auto (GTA), one of the most successful entertainment properties of all time.
Structurally, Take-Two operates through publishing labels such as Rockstar Games, 2K, and Private Division, allowing creative independence while maintaining centralized financial control. This structure enables studios like Rockstar to invest 7-10 years developing a single title, with confidence that returns will justify the investment.
In FY 2025, Take-Two generated $6.22 billion in revenue, marking a ~14 % year-over-year increase. Digital distribution now accounts for the vast majority of its revenue (approximately 96%) as the industry shifts away from physical sales. [9]
8. Epic Games

Headquarters: North Carolina, USA
Revenue: $6 billion+
Key Titles: Fortnite, Infinity Blade
Competitive Edge: Massive player base, Technology licensing and royalty revenue
Epic Games is a major American video game developer, publisher, and technology provider.
Its flagship product, Fortnite, is one of the most successful entertainment platforms ever created. Fortnite has attracted 650+ million registered players, with over 110 million monthly active users across console, PC, and mobile platforms. [10]
Beyond Fortnite, Epic develops and licenses Unreal Engine, a cutting-edge real-time 3D creation technology used by developers around the world to build games, simulations, films, and architectural visualizations.
The company also operates the Epic Games Store, a digital storefront that grew from nearly 108 million users in 2019 to around 295 million registered users by 2024, making it one of the largest PC game marketplaces outside of Steam.
The store attracts developers through a lower revenue cut (typically ~12%) and high-profile exclusivity deals. Plus, Epic has spent billions subsidizing free games and exclusives to build long-term user adoption.
Epic competes with Nintendo primarily through engagement time, cross-platform dominance, and technology influence, rather than direct hardware competition. Fortnite runs on Nintendo platforms but also competes for player attention that might otherwise be spent on first-party Nintendo titles.
7. Valve Corporation
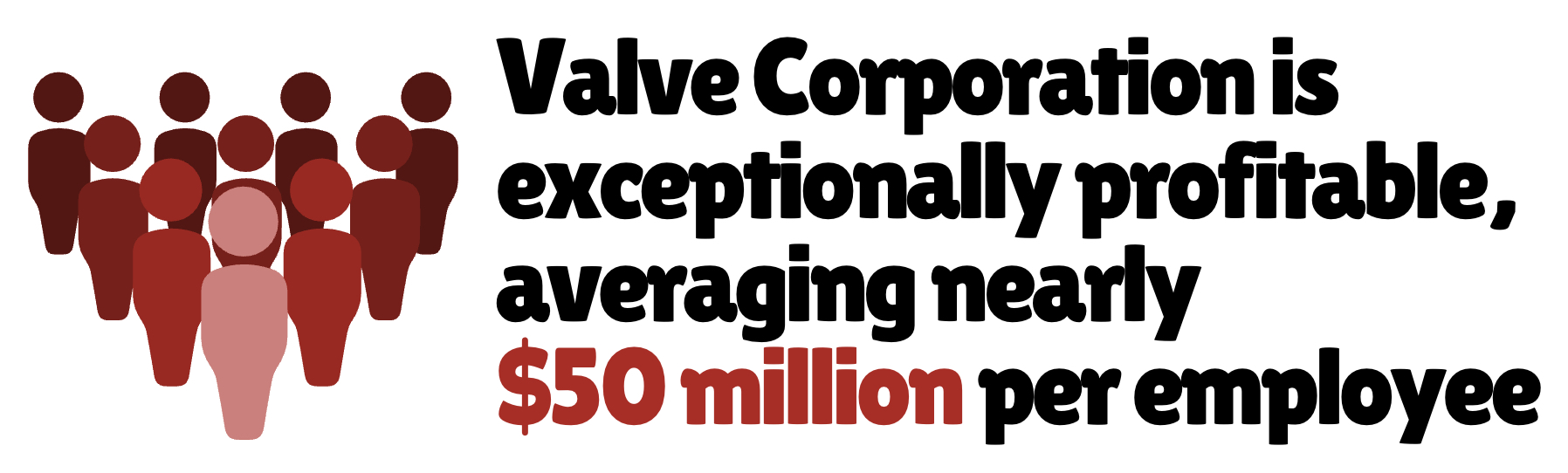
Headquarters: Washington, USA
Revenue: $6.5 billion+
Key Titles: Half-Life, Counter Strike, Dota 2
Competitive Edge: Legacy IP, Exceptional revenue-per-employee
Founded by former Microsoft employees Gabe Newell and Mike Harrington, Valve started as a game development studio and quickly rose to prominence with its debut title, Half-Life.
Over time, it expanded far beyond game creation. In 2003, the company launched Steam, a digital distribution platform for PC games that has since become the world’s largest online games marketplace.
In FY 2025, Steam’s revenue was approximately $17 billion, with Valve’s share (commissions and first-party games) contributing over $4 billion. [11]
Valve’s unique strength lies in its flat organizational structure, where employees self-organize projects without traditional management hierarchies. This model has contributed to unusually high revenue per employee figures compared to other tech giants.
In recent years, Valve expanded into hardware with the Steam Deck, a handheld PC that blurs the line between console and computer. The Steam Deck has sold nearly 4 million units, making Valve a serious contender in portable gaming and indirectly challenging Nintendo’s dominance in the handheld market.
6. MiHoYo
Founded: 2012Headquarters: Shanghai, China
Revenue: $4 billion+
Key Titles: Genshin Impact, Zenless Zone Zero
Competitive Edge: Anime-inspired style, Cross-platform live services
MiHoYo was founded by three students from Shanghai Jiao Tong University who were passionate about games and ACG (anime, comics, and games) culture.
Today, the company (globally branded as HoYoverse) employs over 5,000 people and operates multiple studios and international branches to support game development, publishing, and related services.
MiHoYo’s rise is largely driven by Genshin Impact, one of the most successful games ever released. This game redefined expectations for free-to-play titles by delivering console-quality open-world gameplay without an upfront purchase price. Since launch, Genshin Impact has generated over $5 billion in lifetime revenue.
The company expanded this success with Honkai: Star Rail and Honkai Impact 3rd, building a connected universe of characters, lore, and live-service mechanics.
Technologically, miHoYo invests heavily in proprietary engines, real-time rendering, and AI-assisted content production. It manages large R&D teams focused on animation quality, physical simulation, and character design.
5. Electronic Arts
Founded: 1982Headquarters: Redwood City, California, USA
Revenue: $7.4 billion+
Key Titles: Battlefield, Need for Speed, Madden NFL
Competitive Edge: Live & Esports integration, Strong franchise portfolio
Electronic Arts (EA) pioneered the concept of games as mass-market entertainment products, long before gaming became a global industry worth hundreds of billions of dollars.
Today, the company generates more than $7.4 billion in annual revenue, with a business model increasingly centered on live services, digital distribution, and recurring monetization. [12]
Its portfolio includes sports simulations (EA Sports FC, Madden NFL), shooter franchises (Battlefield, Apex Legends), and sandbox content (The Sims), which broadly caters to different gamer demographics than Nintendo’s usually family-friendly offerings.
In late 2025, EA announced it would be taken private in a $55 billion leveraged buyout, backed by major institutional investors including Saudi Arabia’s Public Investment Fund (PIF), Silver Lake, and Affinity Partners. [13]
4. NetEase Games
Founded: 1997Headquarters: Zhejiang, China
Revenue: $15.5 billion+
Key Titles: Knives Out, Marvel Rivals
Competitive Edge: Deep expertise in MMOs, Strong domestic market
NetEase Games is the interactive entertainment division of NetEase, one of China’s largest internet and technology companies. Its portfolio spans mobile, PC online games, live services, and international publishing, with particularly strong dominance in China and East Asia.
In China, NetEase Games captures roughly 25 % market share of online gaming revenue — second only to Tencent.
The company has built its foundation on massively multiplayer online games (MMOs), many of which have operated continuously for more than a decade. Flagship franchises like Fantasy Westward Journey and Westward Journey Online consistently rank among the highest-grossing PC and mobile games in China.
NetEase also has a strong presence outside China, with game studios in North America, Europe, and Japan. Plus, it partners with major entertainment brands such as Warner Bros. and Mojang to develop games based on well-known franchises, including Harry Potter: Magic Awakened.
3. Microsoft Gaming
Headquarters: Washington, USA
Revenue: $23.5 billion+
Key Titles: Halo, Forza, Minecraft
Competitive Edge: Subscription ecosystem, Cloud gaming reach
Microsoft Gaming is one of the most capitalized players in the global gaming industry. Since launching the original Xbox in 2001, Microsoft has evolved from a traditional console manufacturer into a platform-first, service-driven gaming ecosystem spanning consoles, PCs, cloud infrastructure, and subscriptions.
Its studio portfolio now includes more than 30 internal development teams that have developed extremely successful franchises such as Halo, Forza, Minecraft, The Elder Scrolls, and Diablo.
Plus, Microsoft Gaming has acquired Activision Blizzard for a whopping $68.7 billion, bringing major franchises like Call of Duty, World of Warcraft, and Candy Crush into its portfolio, significantly expanding the breadth and reach of its content offerings. [14]
Microsoft’s key strategy has been its Xbox Game Pass. It offers access to hundreds of games for a monthly fee, including day-one releases for Microsoft’s own studios. In 2025, Game Pass annual revenue exceeded $5 billion. [15]
2. Sony Interactive Entertainment
 Headquarters in San Mateo, California
Headquarters in San Mateo, California
Headquarters: San Mateo, California, USA
Revenue: $31.7 billion+
Key Titles: God of War, The Last of Us
Competitive Edge: Strong first-party IP, Strategic diversification
Since entering the market in the mid-1990s, Sony Interactive Entertainment (SIE) has transformed gaming into a cinematic, premium, global business. Its PlayStation brand has sold over 600 million consoles lifetime.
In fact, the PlayStation has become one of the world’s largest gaming platforms. PlayStation 5 console sold over 84.1 million units worldwide, making it one of the best-selling consoles of its generation. Combined with PlayStation 4, total PlayStation software sales (physical + digital) exceed 1.46 billion units across both platforms.
PlayStation studios produce high-budget exclusives such as God of War, The Last of Us, Spider-Man, and Horizon, with individual titles often selling 10-25 million copies. Development budgets for top PlayStation exclusives often exceed $150 million, rivaling those of Hollywood blockbusters in scale.
SIE’s footprint isn’t limited to hardware. PlayStation platforms have 119 million monthly active users worldwide and more than 51 billion hours of annual gameplay across its installed base.
1. Tencent Interactive Entertainment

Headquarters: Shenzhen, China
Revenue: $27 billion+
Key Titles: Honor of Kings, PUBG
Competitive Edge: Mobile dominance, Ecosystem integration
While Tencent is often associated with social platforms like WeChat and QQ, its gaming division has quietly become one of the largest video game operators by revenue, generating over $27 billion annually from games alone. [16]
It encompasses both internal development studios and external investments. Its publishing arm, Tencent Games, oversees multiple in-house subsidiaries, including influential TiMi Studio Group, and manages global hit games on both mobile and PC platforms.
Tencent’s key titles, such as Honor of Kings, PUBG Mobile, and Clash Royale, have widespread adoption, particularly in mobile markets across Asia and increasingly in the West.
On the other hand, Nintendo’s user base is strong in console ecosystems, but its games rarely match the daily active user scale of Tencent’s free-to-play mobile titles.
Many Tencent games operate on a free-to-play, in-game monetization model, offering cosmetics, seasonal passes, and virtual items that generate ongoing revenue without upfront purchase prices.
Plus, the company leverages its social platforms (QQ and WeChat) to promote and retain players, increase engagement through social features, and cross-sell other digital services.
In recent years, Tencent’s gaming revenue has grown strongly. Recent reports indicate international gaming revenue increased by around 43%, driven largely by popular titles like Delta Force and Valorant, which are performing well across multiple platforms. [17]
Read More
- 18 Best Business Simulation Games | Learn Economics and Strategy
- 10 Fun Math Games That Will Make You Smarter
- 23 Best Physics Games | For All Platforms
- Hardware, A quick history of Nintendo worldwide, Nintendo
- Ali Hussain, How the video game industry is changing, Investopedia
- Industry Report, Global gaming market size and trend analysis, Modor Intelligence
- News, ‘Monopoly GO!’ hit $6 billion revenue milestone, Scopely
- Ivan Mehta, Pokémon GO maker (Niantic) is selling its games division to Scopely, TechCrunch
- Amber V, Developers of the game Dungeon Fighter online go on strike, Automation Media
- Andy Chalk, Arc Raiders sells 4 million copies, PC Gamer
- Company Highlights, Bandai Namco Holdings, Forbes
- Company Financials, Take-Two Interactive’s revenue throughout the years, Macrotrends
- Video Gaming & eSports, Registered users of Fortnite worldwide, Statista
- Anthony Garreffa, Valve makes around $50 million per staffer, TweakTown
- Video Gaming & eSports, Net revenue of Electronic Arts worldwide, Statista
- Alex Ritman, Electronic Arts to go private in $55 billion deal, Variety
- News, Microsoft acquires Activision Blizzard, Microsoft
- Demi Williams, Xbox Game Pass reached ‘nearly $5 billion’ in annual revenue, Techradar
- Naman Ramachandran, Tencent hits $27 billion in revenue driven by gaming and AI investments, Variety
- Market, Tencent goes hands-on to reshape global games empire, The Business Times


